Effect of heat treatment on metastable β Effect of on Micros
date:2021-10-13 09:56 view:
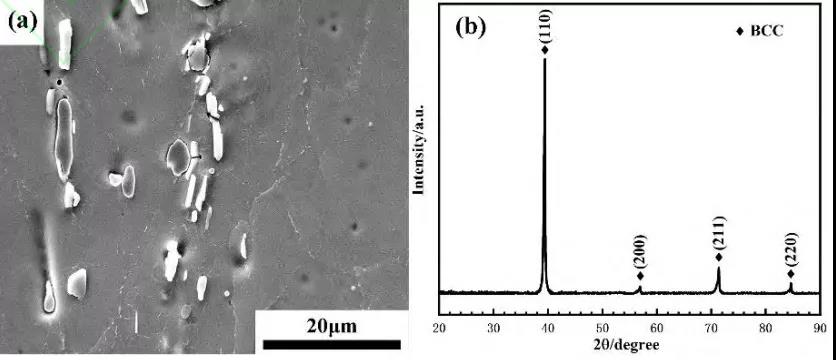
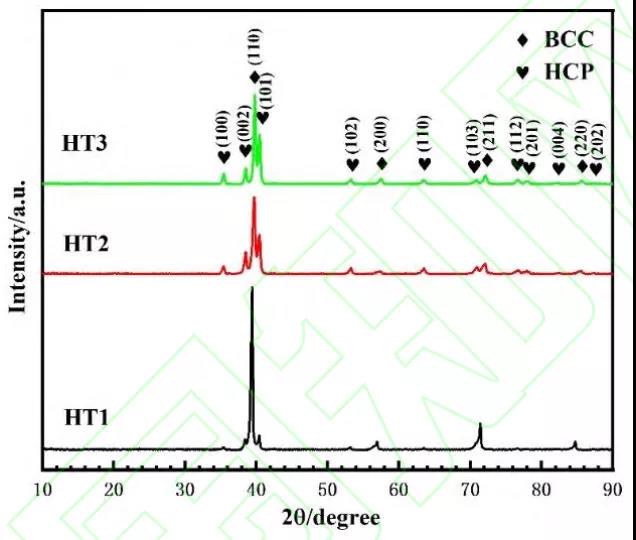
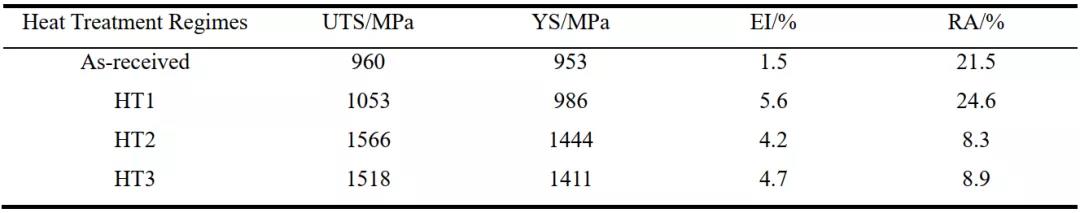
A new metastable alloy with ti-3.5al-5mo-6v-3cr-2sn-0.5fe-0.1b-0.1c was prepared by means of XRD, SEM, TEM, tensile and creep at room temperature β The effects of heat treatment on microstructure, mechanical properties and creep behavior of titanium alloy were analyzed. After solution aging treatment, a large number of acicular secondary particles precipitated in the microstructure of the alloy α Facies, secondary α Phase with β The matrix maintains burgers orientation relationship and semi coherent interface, which significantly strengthens the alloy matrix. The maximum yield strength of the alloy reaches 1444mpa and retains 4.2% elongation. By analyzing the creep test results, it is considered that the creep fracture is distributed on the grain boundary α The stress release caused by the phase is dominated by the fracture mechanism. Grain boundary α The crushing of phase will introduce more positions that may cause holes and cracks, which will worsen the creep resistance of the alloy. Therefore, after solid solution + 300 ℃ aging treatment, the alloy β On grain boundary α The continuous strip distribution of phase makes the alloy have the longest creep life.
prev:Welding skills and quality of pressure vessels made of titan
next:Experience in deformation control of thin wall workpieces
products
news




